### 内容主体大纲1. **比特币钱包的起源** - 比特币的创始背景 - 第一个比特币钱包的上线时间与功能2. **比特币钱包的...
 - Hot wallets vs. cold wallets
- Software wallets, hardware wallets, and paper wallets
3.
- Hot wallets vs. cold wallets
- Software wallets, hardware wallets, and paper wallets
3. 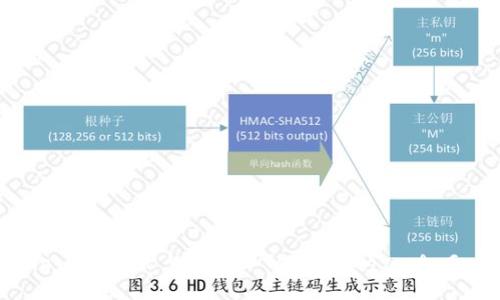 - Common security threats
- Best practices for securing your Bitcoin wallet
5.
- Common security threats
- Best practices for securing your Bitcoin wallet
5. As cryptocurrency continues to grow in popularity, understanding the technology behind Bitcoin wallets becomes essential. At its core, a Bitcoin wallet is a digital tool that allows users to store and manage their Bitcoin. Unlike traditional wallets that carry physical currency, Bitcoin wallets are software programs that interact with the blockchain to facilitate transactions.
Bitcoin wallets are crucial for anyone looking to engage in cryptocurrency trading or secure their investments. They provide the means to send and receive Bitcoin, as well as track your balance and transaction history. Given the decentralized nature of Bitcoin, wallets serve as the bridge between users and the blockchain, making the understanding of their technologies vital.
When it comes to Bitcoin wallets, they can be broadly categorized into two main types: hot wallets and cold wallets. Hot wallets are connected to the internet, making them convenient for daily transactions. Examples include mobile wallets, web wallets, and desktop wallets. In contrast, cold wallets are offline, providing enhanced security, and include hardware wallets and paper wallets.
Software wallets come in various forms, offering flexibility based on user needs. Mobile wallets are popular for their ease of use, while hardware wallets are ideal for long-term storage. Paper wallets represent an interesting option, allowing users to print their keys on paper, thus keeping them entirely offline.
Understanding the functionality of Bitcoin wallets is essential to utilize them effectively. At the core of a Bitcoin wallet is the concept of keys. A Bitcoin wallet contains two keys: a public key and a private key. The public key acts like an email address, allowing others to send Bitcoin to your wallet, while the private key is akin to a password, ensuring that only you can access and manage your Bitcoin.
The transaction process typically involves the wallet broadcasting a transaction request to the blockchain network. The network then verifies the transaction through a process called mining, ensuring that the transaction is legitimate before updating the public ledger. This decentralized verification process is one of the cornerstones of Bitcoin's security model.
While Bitcoin wallets are designed with security in mind, they are not immune to threats. Common security risks include phishing attacks, malware, and hacking attempts. Users must remain vigilant and employ best practices to safeguard their wallets effectively. Using strong, unique passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and constantly updating wallet software are some effective ways to enhance wallet security.
Regularly backing up wallet data and being cautious about sharing private keys are also essential. In particular, users should understand the importance of using cold wallets for long-term storage, which significantly lowers the risk of online theft.
Selecting the right Bitcoin wallet involves assessing various factors, including security, convenience, and functionality. Beginners might prefer user-friendly mobile or web wallets to get started, while advanced users may opt for hardware wallets to maximize security. Researching and comparing wallets based on user reviews, security features, and developer reputation can help make the right choice.
Some popular Bitcoin wallets include Coinbase Wallet, Ledger Nano S, and Trezor. Each wallet comes with its own set of features tailored to different user needs, making it crucial to read through specifications before making a decision.
The future of Bitcoin wallet technology is likely to be shaped by various trends and innovations. One significant trend is the integration of more robust security features, including biometric authentication and advanced encryption. Additionally, as cryptocurrencies gain mainstream acceptance, wallet functionalities will likely expand to support a broader range of digital assets beyond Bitcoin.
Moreover, the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) may lead to the development of wallets that allow users to lend, borrow, and engage in decentralized trading directly from their wallets. Such features will make wallets not just a storage solution but comprehensive financial management tools in the evolving crypto ecosystem.
Q1: What happens if I lose my Bitcoin wallet?
A: Losing a Bitcoin wallet can be catastrophic if you lose your private keys without backups. Always ensure you have your backup phrases stored securely.
Q2: Can Bitcoin wallets hold other cryptocurrencies?
A: Many digital wallets support multiple cryptocurrencies, though this varies by wallet. It’s important to check compatibility.
Q3: Are paper wallets safe?
A: Yes, paper wallets are safe if generated correctly and stored securely. However, they can be lost or damaged, so consider using them alongside other wallet types.
Q4: How do I send Bitcoin from my wallet?
A: You will need the recipient's public address. Enter this in your wallet along with the amount you want to send, and confirm the transaction.
Q5: Is hardware wallet worth the investment?
A: For those holding a significant amount of Bitcoin or concerned about security, hardware wallets are generally worth the investment due to enhanced protection.
Q6: Can I use my Bitcoin wallet for daily transactions?
A: Yes, many people use hot wallets for day-to-day transactions due to their convenience. Always ensure to practice good security habits.
This guide aims to provide comprehensive insight into Bitcoin wallets, showcasing their functions, security aspects, and considerations for potential users. As the cryptocurrency landscape continues to evolve, knowledge of wallet technology will become increasingly important.